Sinoのラミネーションスタックにお任せください!
プロジェクトをスピードアップするために、ラミネーションスタックに以下のような詳細なラベルを付けることができます。 寛容, 材料, 表面仕上げ, 酸化絶縁が必要かどうか, 数量などなど。
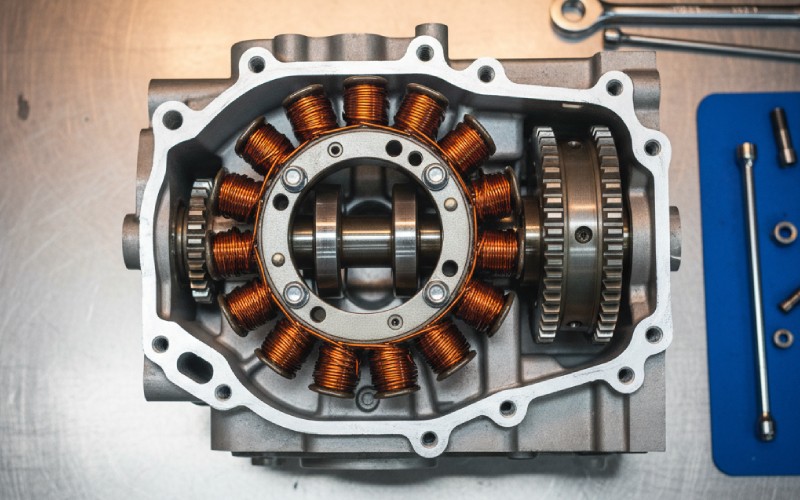
オートバイにもオルタネーターがある?ステーターはオルタネーターと同じですか?これらの質問は少々混乱しやすい。多くのライダーは「ステーター」と「オルタネーター」を同じもののように言う。しかし、これらは同じではありません。違いを知ることは、バイクの電気系統を良好な状態に保つための大きなポイントです。この記事では、ステーターとオルタネーターの主な違いを分かりやすく説明します。それぞれの部品が何をするのか、どのように連動するのか、そしてどのように問題を発見するのかを学びます。これを読めば、整備士に相談しやすくなるでしょう。また、自分のバイクをより大切に扱うことにも役立つはずです。
オルタネーターは発電機の一種。その仕事は電気を作ること。この電気が自動車の電装品に電力を供給する。また、バッテリーの充電も維持します。オルタネーターは現在の自動車にとって非常に重要な部品です。これは普通の車でもバイクでも同じです。オルタネーターが機能しなくなると、バッテリーは急速に電力を失います。するとエンジンが止まってしまいます。
オルタネーターは運動エネルギーを電気エネルギーに変える部品である。オルタネーターはエンジンに接続されており、自動車では通常ベルトで接続されている。エンジンが回転すると、オルタネーター上のプーリーが回転する。この回転が運動エネルギーとなる。オルタネーターはこのエネルギーを電力に変えます。この電力がライト、ラジオ、点火システムを動かします。余分な電気はバッテリーの充電に使われます。これにより、バッテリーは次の始動に備えることができます。
さて、ステーターについて話そう。ステーターは次のような非常に重要な部品である。 内部 オルタネーターオルタネーターはチームであり、ステーターはスター選手の一人だと考えてください。ステーター」という名前は、動かないことから「静止」という言葉に由来する。ステーターはワイヤーのコイルでできた円形をしています。これらのコイルは巻線と呼ばれる。巻線は鉄でできた中心部分に巻き付けられている。この電線のコイルが、電力を作る中心的な部分である。
ステーターはローターと呼ばれる別の部品と連動する。ローターはステーター内で回転する磁石である。ローターが回転すると、その磁場がステーターの銅巻線の上を通過する。この動きによって巻線に電流が流れる。これを電流の「誘導」という。こうしてオルタネーターは電気を作り始める。つまり、ステーターはオルタネーターではありません。ステーターはオルタネーターの動かない部分なのです。
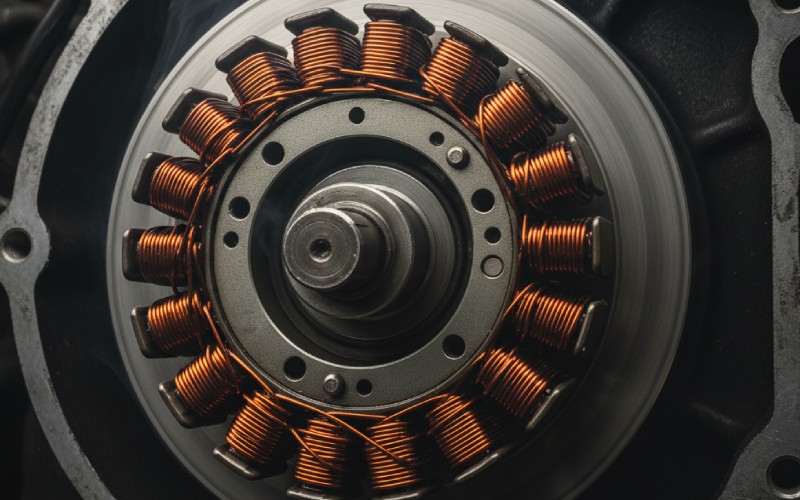

ここが少し厄介なところだ。そう、オートバイにはオルタネーターがある。しかし、オートバイのオルタネーターは自動車のオルタネーターのようには見えません。自動車では、オルタネーターは独立した部品です。エンジンの外側に取り付けられています。ボンネットを開けるとすぐに見える。エンジンのクランクシャフトに接続されたベルトで駆動します。これが多くの人が思い浮かべるオルタネーターのタイプです。
オートバイのオルタネーターは異なる方法で作られている。オルタネーターはエンジンの外側にある独立した部品ではない。その代わり、部品はエンジンに組み込まれている。ローターはクランクシャフトの端に接続されている。ステーターはエンジンケース内にボルトで固定されている。つまり、オートバイにはオルタネーターとステーターがある。システム全体がエンジンの一部なのだ。このように小型化することで、スペースと重量を節約できる。これはモーターサイクルにとって非常に重要なことだ。
最大の違いは簡単に理解できる。ステーターは単一部品。オルタネーターは電気を作るユニット全体です。ステーターがなければオルタネーターは作動しない。そして、ステーターはオルタネーター以外では、単独では何もしない。この2つは同じチームの2つの部品なのだ。電力を作るという仕事をするために一緒に働くのです。
オルタネーターとステーターの違いを見つけるには、それらを比較することが役に立つ。主な違いは、それぞれの仕事とその内容に関係しています。
| 特徴 | オルタネーター | ステーター |
|---|---|---|
| 定義 | 交流電力を作る装置全体。 | オルタネーターの動かない部分。ワイヤーコイルでできている。 |
| 仕事 | 運動エネルギーを有用な電気エネルギーに変える。 | ローターと協力して磁界と電流を作る。 |
| 部品 | ステーター、ローター、整流器、レギュレーターで構成されている。 | 一つの部品(ワイヤーコイル群)である。 |
| 所在地 | 自動車では外側の部品。オートバイではエンジン内部にある。 | オルタネーター内部またはエンジンケース内部にある。 |
つまり、オルタネーターがショーのすべてなのだ。ステーターは一つの演技に過ぎない。誰かが「オートバイのステーター」と言うとき、それは充電システムの特別な一部分を意味する。オートバイのオルタネーター」と言えば、システム全体を意味する。
オートバイのオルタネーターがどのように機能するかは、科学が働いている良い例である。これはすべて、電磁誘導と呼ばれる考え方に基づいている。この考え方は、電気を作ることができることを意味する。磁石をワイヤーのコイルに近づけることで電気を作るのです。モーターサイクル用オルタネーターは、これを利用してバイクに必要な電力を供給します。
エンジンをかけると始まる。エンジンのクランクシャフトが回転し始める。ローターはクランクシャフトに接続されている。ローターは強力な磁石です。クランクシャフトが回転すると、ローターも高速で回転します。ステーターはエンジンケースにボルトで固定されており、動きません。回転するローターはステーターの内側にある。ローターの磁場がステーターのワイヤーコイルを通過すると、コイル内に電流が流れます。これが交流です。この交流電気が、オートバイのオルタネーターが最初に作る電力です。
ステーターは発電の心臓部である。これがなければ電気は生まれない。ローターは一日中回転することができる。しかし、ワイヤーコイルを持つステーターがなければ、磁気エネルギーは行き場を失う。モーターサイクルのステーターは、エンジンから運動エネルギーを受け取る部品である。それを電気エネルギーに変える作業を開始する。
健康なステーターは、電気系統全体にとって非常に重要です。ステーター・ワインディングは非常に高温になります。時間が経つと、ワイヤーのコーティングが壊れることがあります。これにより回路がショートします。するとステーターは電気を作らなくなります。これはモーターサイクルの充電システムによくある問題です。ステーターの不良は、オルタネーターの不良を意味します。つまり、バッテリーに適切な電圧がかからなくなります。バッテリーと電源システムは、健全なステーターに依存しています。
ステーターとローターが注目されることが多いが、オルタネーターが正しく機能するためには、他に2つの部品が必要である。整流器とレギュレーターだ。これらの4つの部品はすべて一緒に動作します。これら4つの部品が一体となって、オートバイのオルタネーター・システムを構成しているのです。これらはすべてチームとして機能します。これらはモーターサイクルに安定した信頼できる電力を供給します。
最初の部品は整流器である。オルタネーターは交流(AC)を作る。しかしモーターサイクルのバッテリーを充電するには直流(DC)が必要です。整流器の仕事は交流を直流に変えることだ。電気の一方通行のようなものだ。交流電流を直流電流に変え、バッテリーがそれを使えるようにするのです。このステップは非常に重要だ。というのも、モーターサイクル上のすべての電気部品が動作するためには直流電力が必要だからです。
番目の部品はレギュレーターである。レギュレーター/レクティファイアと呼ばれることもある。これは、この2つの部品が1つのユニットになっていることが多いからです。レギュレーターの仕事は電圧の量を管理することです。これはオルタネーターがバッテリーに送る電圧です。エンジンの回転数が上がったり下がったりすると、オルタネーターは電力を多くしたり少なくしたりします。もしレギュレーターがなければ、オルタネーターはバッテリーに過大な電圧を送るかもしれません。これではバッテリーが過充電になってしまいます。レギュレーターは、バッテリーが一定の安全な電気量を得られるようにします。これはバッテリーの長寿命化に役立ちます。
オルタネーターとバッテリーは非常に密接に連携している。バッテリーはスターターモーターに電力を供給してエンジンを始動させます。エンジンが始動すると、オルタネーターに電力が供給されます。オルタネーターはモーターサイクルの電気系統に電力を供給します。また、バッテリーに電力を送って充電します。
オルタネーターが機能しなくなると、バッテリーがすべてをこなさなければならない。イグニッション、ライト、その他すべてに電力を供給するが、充電はされない。バッテリーがこの役割を果たせるのはほんの少しの間だけだ。やがてバッテリーは電力不足に陥ります。するとバイクは動かなくなる。オルタネーターが悪いと、道端で立ち往生することになる。そのため、バッテリーが弱っていたり、死んでいたりすると、オルタネーターに問題があることを示す最初の兆候となることが多いのです。バッテリーは正常かもしれません。しかし、オルタネーターがバッテリーを充電する仕事をしていない場合、バッテリーが悪いように見えるでしょう。
オルタネーターやステーターの問題の兆候を知っておくことは良い考えです。問題を早期に発見すれば、道端で立ち往生せずに済みます。悪くなりつつあるオルタネーターは、いくつかの警告サインを示します。
ここでは、オルタネーターに問題があることを示す一般的な兆候をいくつか紹介します:
これらの兆候に気づいたら、充電システムをチェックする必要があります。バッテリーの電圧は、マルチメーターと呼ばれる簡単なツールでチェックできます。エンジンがかかっている状態で、約13.5~14.5ボルトの電圧が表示されるはずです。電圧が低い場合は、オルタネーターの充電が十分ではありません。もっと高い場合は、レギュレーターが壊れている可能性があります。
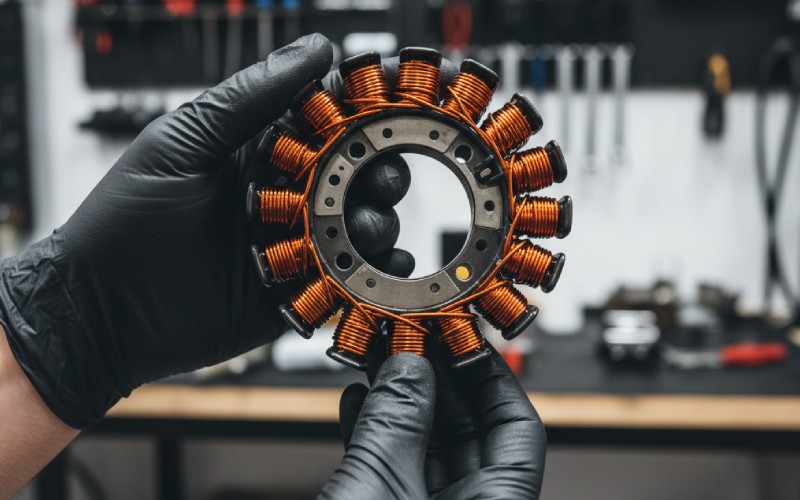

はい、ほとんどの場合、オートバイのステーターだけを交換することができます。オートバイのオルタネーターは、エンジンケース内のさまざまな部品で構成されています。そのため、システム全体を交換する必要はないことが多いのです。ステーターは、オルタネーターで最もよく壊れる部品のひとつです。これはステーターが非常に高温になるためです。
優秀なホームメカニックならステーターの交換はできる。しかし、その作業にはオイルを抜く必要がある。また、エンジンカバーを外さなければならない。内部では通常、ステーターは数本のボルトで固定されている。古いものを外す必要がある。それから新しいものを取り付ける。エンジンの修理が苦手な場合は、バイクを整備工場に持ち込むことをお勧めします。整備士は、充電システム全体をチェックすることができます。そうすることで、異常がステーターだけであることを確認できます。レギュレーターや整流器、あるいはローターが悪くなることもあります。