The Stacking Showdown: Methods, Mastership, and How Sino Delivers
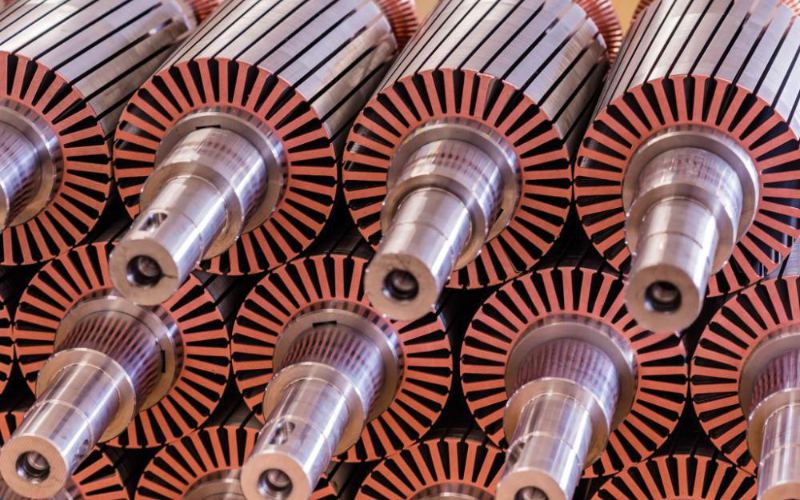
We need stacks of insulated thin sheets. But how do you hold them all together tightly, perfectly aligned, and ready to become the heart of a high-performing motor? This is where the specific technique of rotor lamination stacking becomes critical, and where Sino’s expertise really shines. There are several ways to skin this particular cat, each with its own playbook.
- Welding: The Quick Bond (When Handled with Care)
You’ll often see lamination stacks with neat weld beads running along their outer diameter. TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) or laser welding are common choices here. It can be a fast and cost-effective way to achieve a mechanically robust stack.
- The Upside: It’s relatively quick, lends itself well to automation, and can provide good axial strength. For many general-purpose motors, it’s a solid, economical choice.
- The Catch: Here’s where you need a skilled hand. Welding, by its very nature, involves heat. If not controlled precisely, this heat can locally damage the crucial interlaminar insulation. This can create short-circuits between laminations right at the weld zone, leading to increased localized eddy current losses and unwanted hotspots – exactly what we’re trying to avoid! It can also subtly alter the magnetic properties of the steel near the weld.
- Sino’s Approach: At Sino, when welding is the chosen route for a rotor lamination stacking project, we employ advanced, controlled welding processes. This includes precise parameter settings, often utilizing laser welding for its minimal heat-affected zone, and rigorous post-weld inspection. We understand the metallurgy of the electrical steels we work with, ensuring we minimize any negative impact.
- Real-World Scenario: A client producing robust industrial pump motors needed a cost-effective stacking solution for medium-volume production. Our optimized TIG welding process, combined with strategic weld placement and quality checks, delivered the mechanical integrity they needed without significantly compromising the core loss performance, keeping their unit costs competitive.
- Interlocking (Stitching/Stamped Features): The Mechanical Lock-In
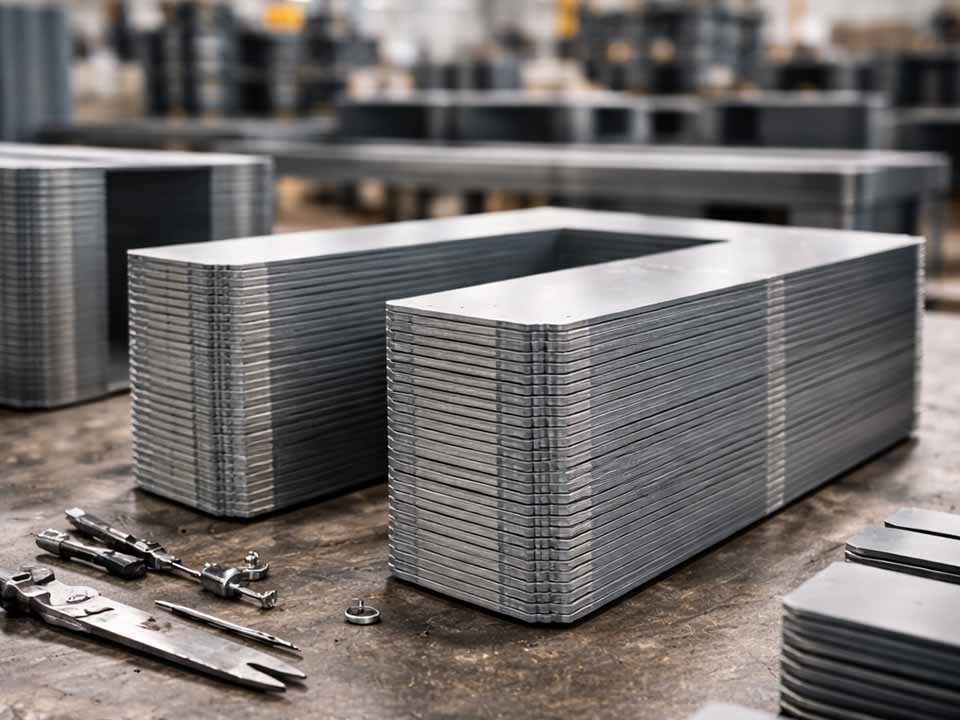
Think of this like tiny metal Lego™ bricks. During the stamping process where each lamination is cut to shape, small protrusions (bumps or “dimples”) and corresponding recesses are formed directly into the steel. As you stack them, these features interlock, creating a mechanically joined core.
- The Upside: A huge plus is that there’s no heat involved in the joining process itself, so the interlaminar insulation remains pristine across the entire lamination surface. This is fantastic for preserving electrical performance. It’s also a very automation-friendly technique, great for high-volume production.
- The Catch: Those little interlocking features, while clever, do take up a tiny bit of space that could otherwise be magnetic steel. This slightly reduces what’s called the “stacking factor” – the ratio of actual magnetic material to the total stack volume. Also, the stamping process for these features needs precise tooling and can sometimes introduce minor stresses into the laminations.
- Sino’s Approach: We’ve invested heavily in precision tooling and stamping technology. For interlocking rotor lamination stacking, our dies are engineered to create clean, consistent interlocks that maximize holding power while minimizing material displacement. We also advise clients on how the interlocking pattern might influence magnetic flux paths.
- Real-World Scenario: A manufacturer of servo motors for automated packaging lines required extremely consistent rotor geometry and minimal core losses. Our interlocking solution provided the tight tolerances and excellent electrical insulation they needed for high-speed, precision movements, and our high-speed stamping lines met their volume demands.
- Bonding (Adhesives/Backlack): The Ultimate Insulated Union
This is where things get really sophisticated. An adhesive coating, often called “backlack” or “bondable insulation,” is applied to one or both sides of the lamination sheet before it’s stamped. After stacking, the entire assembly is subjected to heat and pressure in a curing process. This activates the adhesive, bonding the laminations into an incredibly solid, yet still perfectly electrically insulated, unit.
- The Upside: This method is often considered the gold standard for electrical insulation integrity between laminations. It results in a very rigid, dimensionally stable stack, which is great for reducing noise and vibration. The adhesive can also help to dampen mechanical resonances.
- The Catch: It’s generally a more involved process. The application of the adhesive, the careful handling of coated material, and the curing cycle (time, temperature, pressure) add complexity and can increase the per-unit cost compared to simpler methods.
- Sino’s Approach: Sino has dedicated clean-room facilities and specialized curing ovens for adhesive bonding. We work with various grades of backlack, matching the adhesive properties to the motor’s operating temperature and environmental conditions. Our precise control over the curing process ensures a complete and uniform bond, leading to superior performance in demanding scenarios like high-efficiency EV motors or quiet appliance motors. This advanced rotor lamination stacking is a cornerstone of our offering for premium applications.
- Real-World Scenario: A high-end electric vehicle manufacturer approached us to produce rotor cores for their next-gen powertrain. Their key requirements were maximum efficiency, minimal noise (NVH), and high rotational speed capability. Our adhesive bonding process using a specialized high-temperature backlack delivered exceptional results, contributing to their vehicle’s impressive range and quiet operation.
- Cleating or Riveting: The Old Guard (Still Kicking for Some)
These are more traditional mechanical fastening methods. Cleating involves forcing strips of metal into axial grooves punched or machined into the stack’s periphery. Riveting, as the name suggests, uses rivets passed through holes in the laminations to clamp them together.
- The Upside: For certain designs, especially older ones or very large, low-speed industrial motors, these can be straightforward and robust solutions.
- The Catch: Both methods inherently reduce the active magnetic material (lowering the stacking factor) because of the space taken by the cleats/rivets and their associated holes. They can also be more labor-intensive and might not be the best choice for high-speed motors where balance and minimizing windage losses are critical. Over time and under thermal cycling, there’s also a slight potential for looseness to develop.
- Sino’s Approach: While we see these methods less frequently for new, high-performance designs, Sino maintains the capability to produce cleated or riveted stacks for legacy applications or specific customer requirements. We ensure precise alignment and secure fastening to maximize the performance achievable with these techniques.
Here’s how these common rotor lamination stacking methods stack up, if you’ll pardon the pun:
Stacking Method | Sino’s Focus & Expertise | Key Advantages | Potential Trade-offs | Ideal Scenarios |
Welding | Advanced, controlled laser/TIG welding; minimized heat-affected zone; stringent QC. | Cost-effective for many volumes, good axial strength, automation friendly. | Requires careful control to avoid insulation damage & localized losses. | General industrial motors, pumps, fans. |
Interlocking | Precision tooling, optimized interlock design for strength & stacking factor. | Excellent insulation integrity, highly automatable, consistent geometry. | Minor reduction in stacking factor, specific tooling required. | Servo motors, high-volume appliance motors, robotics. |
Bonding (Adhesive) | Clean-room application, specialized backlack grades, precise curing protocols. | Superior insulation, high mechanical stability, excellent NVH characteristics. | Higher process complexity and cost, curing time. | EV/HEV traction motors, high-efficiency motors, quiet applications. |
Cleating/Riveting | Precision alignment, secure fastening for legacy or specific large-scale designs. | Simplicity for certain designs, robustness in specific low-speed scenarios. | Reduced stacking factor, potential for looseness, higher labor for some. | Large industrial motors (legacy), specialized machinery. |
Sino's Edge: It’s More Than Just Putting Plates Together
At Sino, we believe that exceptional rotor lamination stacking isn’t just about mastering one technique; it’s about understanding the entire ecosystem.
- Material Savvy: We don’t just stack what we’re given. We work closely with you, and with leading electrical steel producers (like those documented by World Steel Association reports on advanced grades), to select the optimal lamination material and insulation coating for your specific performance targets, operating temperatures, and frequency requirements. Thinner gauges for high frequency? Special coatings for corrosive environments? We navigate these choices daily.
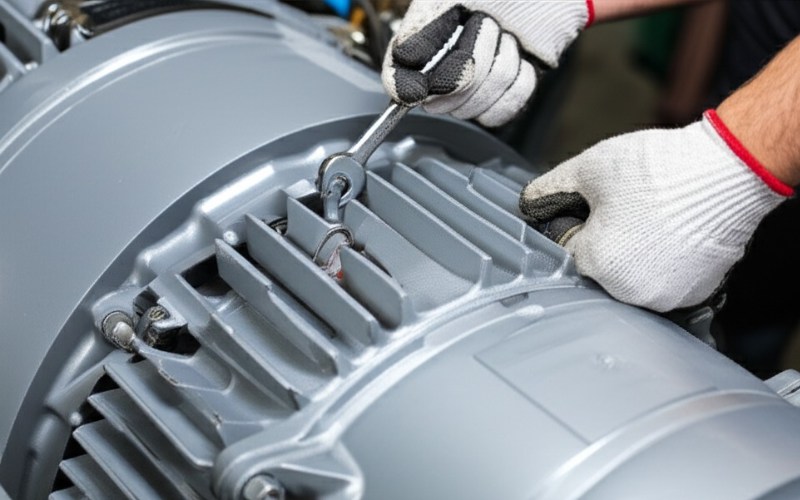
- Tooling Prowess: The quality of a stack starts with the quality of the individual lamination. Our in-house tooling design and fabrication capabilities mean we produce incredibly precise laminations with minimal burrs. Burr height is a silent killer of insulation, and we’re obsessed with keeping it near zero.
- Quality at Every Step: From incoming material inspection to final stack dimension and electrical testing, quality control is embedded in our DNA. We employ vision systems, CMMs (Coordinate Measuring Machines), and specialized electrical test rigs to ensure every stack leaving our facility meets or exceeds your specifications. This means better fit-up in your motor assembly, more consistent magnetic properties, and ultimately, a more reliable end product.
- Customization is King: Got a unique rotor geometry? Need integrated features like magnet pockets for an IPM (Interior Permanent Magnet) rotor? We thrive on these challenges. Our engineering team collaborates with yours to develop custom rotor lamination stacking solutions that are perfectly tailored.
Real-World Impact: Where Sino's Rotor Lamination Stacking Drives Success
The principles of excellent rotor lamination stacking aren’t just theoretical; they deliver tangible benefits across a vast array of scenarios.
- Electric Mobility Revolution: In the demanding world of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), every percentage point of efficiency translates to greater range, and every decibel of noise reduction enhances driver comfort. Sino’s proficiency in adhesive bonding and ultra-thin lamination stacking is crucial here. We help EV motor designers achieve the high power densities and smooth torque delivery that modern electric powertrains demand.
- The Unseen Workhorses of Industry: Think about industrial automation – robots on an assembly line, conveyor systems, precision machine tools. These systems rely on motors that deliver precise motion, cycle after cycle, often 24/7. For these scenarios, the robustness and consistency from well-executed interlocking or welded rotor lamination stacking are key. We ensure that the stacks we produce contribute to the long operational life and minimal downtime that these industrial applications demand.
- Powering Our Daily Lives: From the quiet hum of your high-efficiency washing machine to the reliable chill of your refrigerator compressor, electric motors are everywhere. For appliance manufacturers, cost-effectiveness, energy efficiency (think Energy Star ratings), and low noise are paramount. Sino delivers rotor lamination stacking solutions that help these manufacturers meet stringent regulatory requirements and consumer expectations, often utilizing optimized welding or high-volume interlocking.
As highlighted in many engineering texts, such as the “Electric Motors and Drives: Fundamentals, Types and Applications” by Hughes and Drury, the construction of the magnetic core is a fundamental determinant of motor characteristics. We take that principle to heart in every stack we produce.
Looking Ahead: The Evolving Landscape of Lamination Stacking
The world of electric motors isn’t standing still, and neither is the technology of rotor lamination stacking. We’re seeing trends towards:
- Even Thinner Laminations: For higher frequencies and even lower core losses.
- Advanced Electrical Steels: With improved magnetic properties and lower specific losses.
- More Sophisticated Insulation Coatings: Offering better dielectric strength, thermal conductivity, or self-bonding properties.
- Increased Automation and “Smart” Stacking: Using real-time feedback to optimize the stacking process.
Sino is not just keeping pace; we’re actively investing in R&D and process improvements to stay at the forefront of these advancements. Our commitment is to provide you with rotor lamination stacking solutions that are not just for today’s motors, but for tomorrow’s innovations too.
Your Partner in Peak Motor Performance: Choose Sino
So, when you’re designing your next electric motor, or looking to improve an existing one, remember that the humble-looking stack of laminations at its core holds immense potential. The way those laminations are selected, processed, and assembled – the entire rotor lamination stacking process – is a critical lever for performance, efficiency, and reliability.
At Sino, this isn’t just a manufacturing step; it’s our specialty. We combine deep technical expertise, state-of-the-art technology, and a genuine passion for problem-solving to deliver rotor cores that help your motors perform at their absolute best.
Ready to see how Sino’s approach to rotor lamination stacking can elevate your next project? Let’s talk. We’re confident that our capability can make a real difference.