Let Sino's Lamination Stacks Empower Your Project!
To speed up your project, you can label Lamination Stacks with details such as tolerance, material, surface finish, whether or not oxidized insulation is required, quantity, and more.
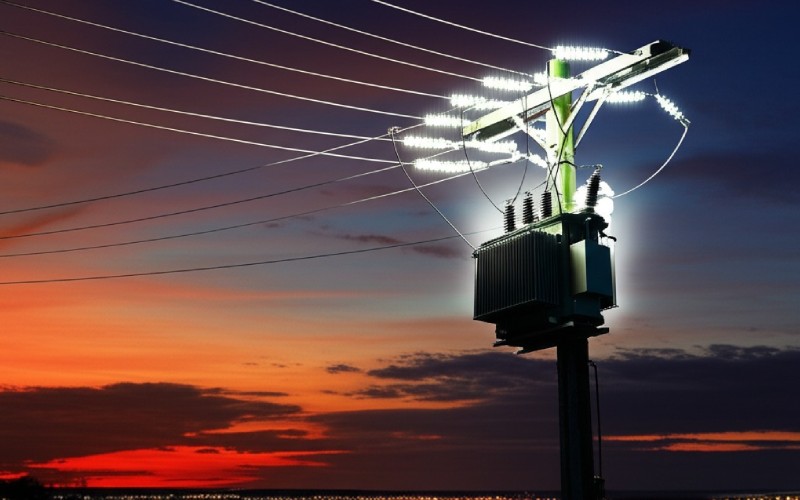

Distribution transformers are the quiet workers of our power distribution system, bringing power to our homes and jobs. This complete guide is for anyone who wants to learn about these important machines. I will show you what they are, how they work, and the different kinds, all in easy words. You should read this because knowing about a distribution transformer helps you see the long trip power takes to reach you.
A distribution transformer is a main part of the electrical power system. It does the last voltage change before power comes to you, the user. You can think of it as the final stop for electrical energy on its way to your house or work. It’s a type of transformer that takes the high voltage from the distribution lines and “steps it down” to a lower, usable voltage. Without these machines, the high-voltage electricity moving through the power grid would be too strong for your TV, lights, and other things. This complete guide will tell you all you need to know.
In simple words, it is a machine that moves electrical energy from one circuit to another. It also changes the voltage level when it does this. This works because of a rule called electromagnetic induction. A distribution transformer has two main sets of coils, also called a winding, wrapped around a magnetic iron core.
The work starts when an alternating current (AC) flows through the first coil. This is the primary winding. This flow makes a changing magnetic field in the iron core. This magnetic field then makes a voltage in the second coil. This is the secondary winding. The secret is the number of turns in each coil. To make a lower voltage, the secondary winding has fewer turns than the primary winding. This is why a distribution transformer is a step-down transformer. It lowers the voltage to a safe level for use in homes.
In my job, I have used many different types of distribution transformers. We can group them in different ways. We can group them by where they are put, what they use for insulation, and how many phases they work with. Each type of transformer is made for certain jobs and places.
Here is a list of the common types of distribution transformers:
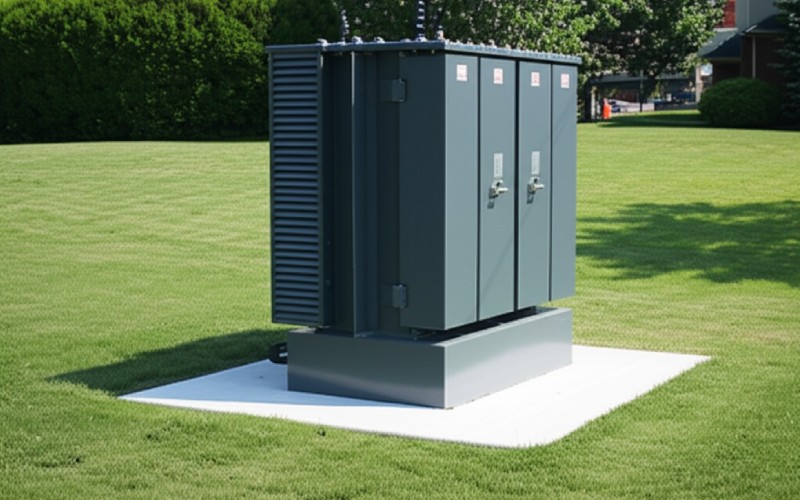

The applications of distribution transformers are many and are key to our daily lives. I have seen them used in almost every place you can think of. Their main purpose is to take the high-voltage power from the distribution network and make it safe for us to use.
Some key applications of distribution transformers are:
I said that a distribution transformer is a step-down transformer, but how does it lower the voltage? It is all about the number of turns in the primary and secondary windings. A step-down transformer has more turns in its primary coil than in its secondary coil.
When a high voltage goes into the primary winding, it makes a strong magnetic field. This magnetic field then moves across the secondary winding and creates a voltage. Because the secondary winding has fewer turns of wire, the voltage it makes is lower. This is based on Faraday’s Law of Induction. The speed of the electrical energy stays the same; only the voltage and current levels are changed. This easy but smart idea lets us have safe electrical power.
In my work, I see that people often mix up a power transformer and a distribution transformer. Both are needed for the power grid, but they do different jobs. A power transformer is used in transmission lines to step up the voltage to send power very far. It can also be used to step down voltage at a substation. They work with very high voltage, sometimes 400kV or more.
A distribution transformer is the last part of the trip. It takes the lower voltage from the distribution lines (like 11kV or 33kV) and steps it down to the voltage people use (like 240V). So, the main differences are their voltage levels, their size, and where they are in the power distribution system. A power transformer is very big and is at power plants and big substations. A distribution transformer is smaller and is closer to where people live and work.
| Feature | Power Transformer | Distribution Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Job | Steps up or steps down voltage for sending power | Steps down voltage for final use |
| Voltage Level | High voltage (like 66kV, 200kV, 400kV) | Lower voltage (like 11kV, 33kV) down to 240V/400V |
| Size | Bigger in size | Smaller in size |
| Place | Power plants and transmission substations | Near homes, stores, and factories |
| kVA Rating | Usually more than 5000 kVA | Usually less than 200 kVA, up to 5000 kVA in some cases |
Choosing a single-phase or a three-phase distribution transformer depends on how much power is needed. I have put in both kinds in different electrical systems. A single-phase transformer is used for single-phase power, which is normal for homes and small shops. It has one primary winding and one secondary winding.
A three-phase transformer is used for a three-phase power supply. This is standard for most factories and stores that need more power. A three-phase distribution system is a better way to send power over long ways. These transformers have three sets of windings for both the primary and secondary sides. Using three-phase power gives a steady power supply. This is very important for running big motors and other heavy machines.
I have been to a transformer manufacturer plant, so I can tell you that building a distribution transformer is a detailed job. The center of the transformer is the magnetic core. It is made of thin sheets of silicon steel. Building it in layers helps stop energy loss from what we call eddy current and hysteresis.
The primary and secondary windings are coils of copper or aluminium wire with a cover. These windings are neatly wrapped around the core. The whole thing is put inside a strong tank that is usually filled with a special oil. This oil does two things: it gives insulation between the winding parts and the tank, and it helps cool the transformer. It moves the heat away that is made while it works. Other key parts are bushings to connect the high and low-voltage wires, a safety valve for pressure, and sometimes a tool to change the voltage a little bit.
If you look around your area, you will probably see either pole-mounted or pad-mounted transformers. Pole-mounted transformers are the ones you see up on utility poles. They are common in places with overhead power lines, like in the country or some neighborhoods. A good thing about pole-mounted transformers is that they do not use any space on the ground.
Pad-mounted transformers, on the other hand, sit on a concrete block on the ground. They are used with power lines that are under the ground. You can find them in city areas, new home areas, and near stores. The transformer is inside a locked metal box. This makes it safer and look better. The choice between the two often depends on things like space, safety, and the kind of power distribution lines being used.
Choosing a reliable distribution transformer is very important to get a safe and steady power supply. As a person who has bought many transformers, I can tell you it’s a big choice. You must think about a few things to get the right power solutions for what you need.
First, you need to find the right kVA rating. This tells you how much power the transformer can handle. This depends on all the electrical things it will give power to. You also need to think about the primary and secondary voltage your electrical system needs. Other important things are the type of insulation (oil-filled or dry-type), if you need a single-phase or three-phase transformer, and where it will be put (pole-mounted or pad-mounted). It is also smart to pick a good transformer manufacturer. A good one has a history of making great products and services. Look for papers that prove its quality and a history of good help for buyers.
Here are some key things to remember when you pick a distribution transformer:
To sum up, the distribution transformer is a basic part of our electrical world. It does a very important job in the safe and good power distribution we use every day. From the simple ideas of electromagnetic induction to the different kinds and uses, I hope this complete guide has helped you better understand these important electrical machines.