Let Sino's Lamination Stacks Empower Your Project!
To speed up your project, you can label Lamination Stacks with details such as tolerance, material, surface finish, whether or not oxidized insulation is required, quantity, and more.
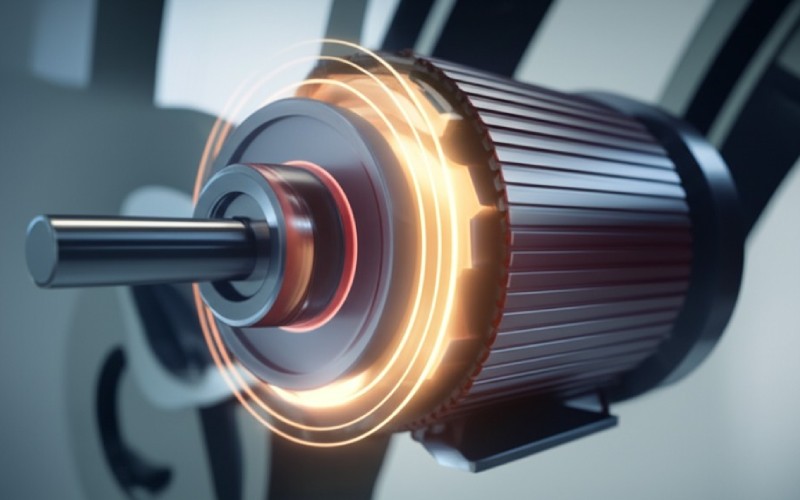
Allow me to inform you, the AC motor is a real celebrity. You find this impressive electric motor in numerous places, from the fan that cools you to the large devices in factories. This post is going to be your easy overview of the AC motor. We’ll discuss what an AC motor is, just how it does its task, the different types of AC motor options you have, and why selecting the right AC motor matters a whole lot. If you have actually ever been curious about these powerful tools, or if you need to pick an AC motor for something you’re building, then you’re in the best place. I’ll aid you recognize the AC motor so you can see exactly how helpful it is.
You might be asking, “What is an AC motor, actually?” Well, it’s rather straightforward when you break it down. An AC motor is an electrical machine. This electrical motor runs on something called alternating current (AC). We get this AC power from the outlets in our house, commonly at a specific AC voltage that drives the current. So, an AC motor is a gadget that transforms electrical energy from this alternating current into motion– the rotating kind of motion that can do work. Think of fans, pumps, or anything that requires rotation. That’s typically an AC motor getting the job done. This type of electrical motor is very common.
There are many types of electric motors in my day, but the AC motor stands out for its wide usage. It takes that alternating current, which, as the name suggests, alternates or changes direction many times a second, and uses it to create torque. This torque makes a part of the AC motor spin. It’s a brilliant little design that powers so much of our modern lives. An AC motor is a real workhorse. An AC motor is essential.
So, just how does an AC motor actually transform power right into spinning motion? It resembles a bit of magic, but it’s all science! The key is something called a rotating magnetic field. When you feed alternating current into an AC motor, it produces this unique magnetic field inside the motor. This field isn’t still; it rotates around. Picture holding a magnet and rotating it in a circle. That’s sort of what’s happening inside the AC motor. This AC motor utilizes a fascinating principle.
This rotating magnetic field is extremely important for the motor operation. There’s another component inside the AC motor, called the rotor, that wants to follow this spinning field. Consider it like a dog chasing its tail, or a compass needle trying to follow a magnet you’re moving. The rotor gets pulled along by the rotating magnetic field, and that’s what generates the rotating motion. This is how the motor runs on a fundamental level. This is the fundamental concept behind most AC motor designs. The method for this motor operation is really clever for an AC motor.
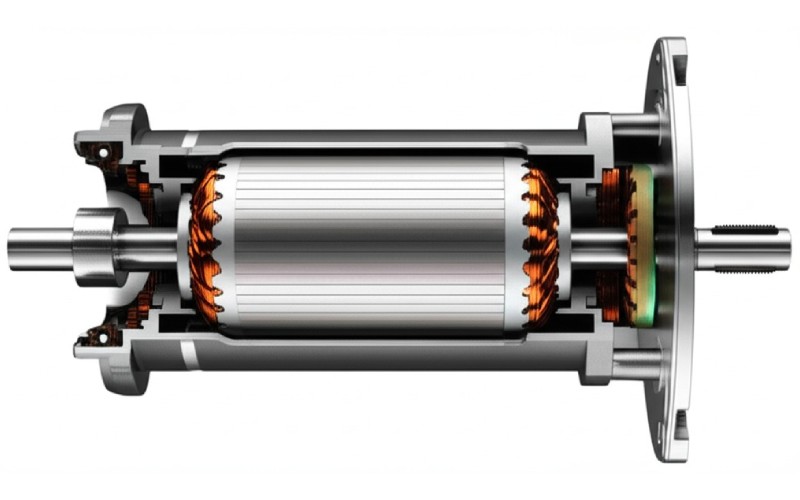
Every AC motor has a couple of major stars in its show. AC motors have two main parts. These are called the stator and the rotor. The stator is the outside part of the motor that remains still. It has coils of wire in it. When alternating current flows through these coils, the stator creates the rotating magnetic field we just spoke about. The elements of an AC motor are rather straightforward. You can consider the stator as the stage where the magic happens in an AC motor.
The rotor is the internal part of the AC motor that rotates. It’s attached to the motor shaft, which is the component that sticks out of the AC motor and does the real work, like rotating a fan blade. The rotor is affected by the stator’s magnetic field. The AC electromagnets on the stator pull the rotor around. There are different sorts of rotors, which lead to different AC motor types, but the definition of a stator and a rotor is true for nearly every AC motor.
You might ask yourself why the AC motor is such a big deal. Well, electric motors are used in numerous devices, and the AC motor is often the top choice. One big reason is that AC motors are generally made use of because they are often simpler in design compared to some other types. Fewer parts can mean less to go wrong. This often makes the AC motor very reliable and long-lasting.
Another reason electric motors are widely adopted, specifically the AC motor, is their good motor efficiency. They do a great job of converting electrical energy into motion without wasting too much energy as heat. Plus, they can be made at a lower cost for many applications. AC motors are versatile, meaning they can be used for a lot of different tasks, from small household appliances to large industrial machines. These electric motors also tend to be economical for many power ranges. This versatility and reliability make the AC motor a very commonly used solution. The AC motor is just a smart choice for many scenarios.
Now, not all AC motors are the same. Similar to there being different kinds of cars, there are different kinds of AC motors. We can put AC motors into a few main groups. The two main sorts of AC motors you’ll find out about most are induction motors and synchronous motors. These are the main types of AC motor you will find. Usually, we speak about induction motors and synchronous motors as the key categories. Understanding these categories for AC motors can help you select the best AC motor for a task.
Within these large groups, there are even more specific types of electric motors. For instance, AC motors can also be grouped by the type of power supply they use. Some AC motors run on single-phase AC power, which is common in homes. Others, particularly larger ones used in industrial settings, use three-phase AC power, which is a type of multiphase AC. The types of electric motors we commonly see, these motors include options like single-phase AC motors for homes and heavy-duty three-phase versions for industries. Each type of AC motor has its own strengths and is good for specific tasks. So, when you hear about different types of AC motor, remember these key distinctions. An AC motor can be quite specific.
Let’s delve into the induction motor. This is probably one of the most common types of AC motor you’ll find. The induction motor is a type of AC motor that is incredibly popular. In fact, when people talk about an AC motor, they’re often thinking of an induction motor. The induction motor is also sometimes called an asynchronous motor. “Asynchronous” means it doesn’t rotate at the exact same speed as the rotating magnetic field in the stator. There’s a little slip, which is actually how the motor uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to create torque in the rotor. An induction motor is a very clever type of AC motor. This type of AC motor is seen almost everywhere.
The magic of the induction motor happens because the stator’s rotating magnetic field induces a current in the rotor without any direct electrical connection, like brushes. This induced current creates its own magnetic field in the rotor, which then tries to catch up with the stator’s field, making the induction motor spin. Many AC induction motors use a design called a squirrel cage motor. This type of induction motor has a rotor that looks like a cage for a squirrel; the motor takes its name from this shape! These electric motors use the squirrel-cage rotor because it’s simple and robust. These motors will certainly often use cast aluminum or copper for the rotor bars. You’ll find the induction motor in everything from washing machines (often a single-phase induction motor or split-phase induction motor) to factory conveyors (usually a three-phase induction motor). Some AC motors use the squirrel-cage design very efficiently. We also have wound-rotor motors or wound-rotor induction motors, which offer more control over speed and torque, but are a bit more complex than the common induction motor. The AC induction principle is fundamental to many AC motor designs. This induction motor is a marvel.
Now, let’s look at the other main player: the synchronous motor. This type of AC motor is a bit different from the induction motor. The biggest difference is right in the name: “synchronous.” This means the synchronous motor rotates at a speed that is exactly locked, or synchronized, with the speed of the rotating magnetic field created by the stator. There’s no slip like in an induction motor. The motor speed of a synchronous motor is very precise. This AC motor keeps perfect time with the current.
Unlike the induction motor, the synchronous motor doesn’t rely on the induced current in the rotor to create torque in the same way. Instead, the rotor of a synchronous motor typically has its own magnets. These can be permanent magnets (motors with permanent magnets) or electromagnets that get their power from a separate DC power source. Because the rotor has its own strong magnetic field, it locks onto the stator’s rotating field and rotates completely in synchrony. Synchronous motors are great for applications that require precise speed control, like in clocks, timers, or special industrial machinery. You might also find a reluctance motor, which is a special type of synchronous motor that works without permanent magnets or a separate DC supply for the rotor. A synchronous motor is a vital AC motor.
The biggest clue is in their names. An AC motor runs on alternating current, where the electrical power changes direction back and forth. A DC motor, on the other hand, runs on direct current (DC). The AC power advantage is its wide availability, while a DC motor uses DC power. This fundamental difference in power supply impacts how each motor is designed and how it functions. This AC motor connects right into the wall socket/outlet.
Many DC motor designs use something called brushes to get power to the spinning part (the rotor). These brushes can wear out over time. Many AC motor types, especially induction motors, do not use brushes. This often makes the AC motor simpler and require less maintenance. However, DC motors can offer great speed control and high starting torque. There are also brushless DC motor options now, often called a BLDC motor. The BLDC motor is very efficient. However, for many general uses, the AC motor is preferred for its simplicity and direct use of available alternating current. A BLDC motor is a good alternative, but the AC motor remains popular. The DC motor has its place, but the AC motor is a workhorse. You might also find out about a BLDC motor in some modern tools powered by DC power.

So, where do we really see all these AC motors in action? The answer is: almost everywhere! AC motors are used in a massive range of applications. In your house, an AC motor may be humming away in your fridge, washing machine, dishwasher, fans, and air conditioner. These are typically single-phase AC motor types because that’s the power supply we have at home. Many appliance motors operate on a single-phase supply. The AC motor is very common in household appliances.
In factories and industrial applications, AC motors are even more common. They power pumps, conveyor belts, mixers, compressors, and all types of equipment. These are often larger, more powerful three-phase AC motor devices because industrial sites generally have three-phase AC power available. Motors are frequently used here due to their robustness. For any specific application, there’s likely an AC motor designed for it. They are ideal for applications requiring consistent power. Making them optimal for applications that run for long hours, motors can be used reliably. Motors are also used in electric vehicles, though often these are specialized AC motor designs or even BLDC motor types. Indeed, AC motors are becoming more advanced with new control technologies. The versatility means AC motors are widely used. For many applications that require motion, an AC motor is the go-to.
Have you ever wondered how AC motors are made? The motor design includes careful winding of copper wires for the stator coils and precise construction of the rotor. The materials used and the precision of manufacturing impact the motor performance and lifespan of the AC motor. It’s a mix of good design and skilled assembly. The AC motor is an item of careful work.
A very important thing about an AC motor is its motor speed. What controls the speed of an AC motor? For most AC motors, especially common AC motor types like induction and synchronous ones, the speed is primarily determined by two things: the number of “poles” in the motor design and the frequency of the AC supply (the power supply). In many places, like the U.S., the frequency is 60 Hertz (Hz), meaning the current changes direction 60 times a second. In other areas, it’s 50 Hz. Changing this frequency (often with a device called a variable frequency drive or VFD) is a common method to control the speed of the motor. The speed of the AC motor can therefore be carefully tuned. For an AC motor to function well, the motor must be matched to its load. Proper motor starting is also crucial for many AC motor applications to prevent issues. An AC motor can be started in various ways depending on its size and type. The motor shaft provides the power at this controlled speed. The speed of the AC motor is a key feature of any type of AC motor.