Let Sino's Lamination Stacks Empower Your Project!
To speed up your project, you can label Lamination Stacks with details such as tolerance, material, surface finish, whether or not oxidized insulation is required, quantity, and more.
This article will introduce you to two kinds of electric motors. One is the axial flux motor. The other is the radial flux motor. They both make things spin. But they work in very different ways. Why should you read this? Because if you understand these types of motors, you can make smart choices. Maybe you are building something cool. Or maybe you just like to know how stuff works. I’m going to show you what makes each motor special. We will look at motor design. We will discover the differences in how the magnetic magic happens in each motor. Let’s find out which one might be better for you!
An axial flux motor is a bit like a flat pancake. The parts inside this axial flux motor are flat too. The spinning part is called a rotor. The part that stays still is called a stator. In an axial flux motor, the magnetic power, or axial flux, goes straight along the line of the motor’s axle. Think of an axle like the stick in the middle of a wheel. In an axial flux motor, the flat stator and rotor discs are side by side. The magnetic force acts straight across, perpendicular to the discs.
So, why is this axial flux motor special? Its flat shape is a big deal. This axial flux motor can be very thin. This means it can fit in tight spots. The stator in an axial flux motor often has coils of copper wire. These wires and the magnet parts create a strong magnetic field. This field makes the rotor spin. This type can be powerful. We will discover the differences when we compare it with another motor. The potential of axial flux motors is huge.
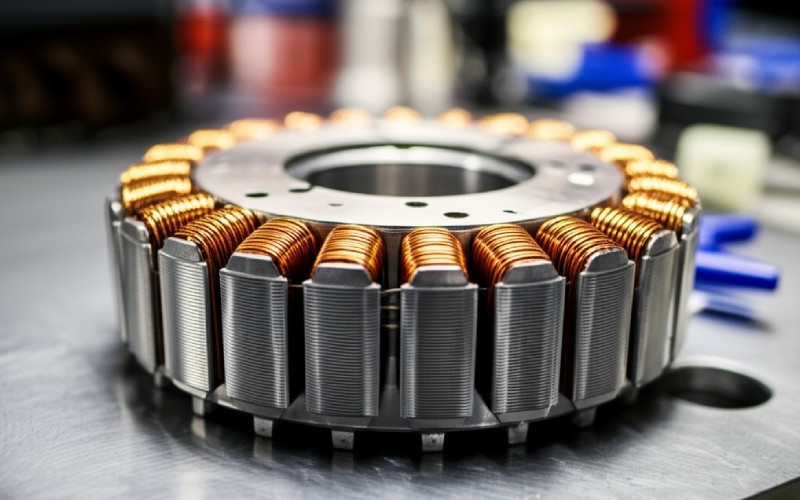

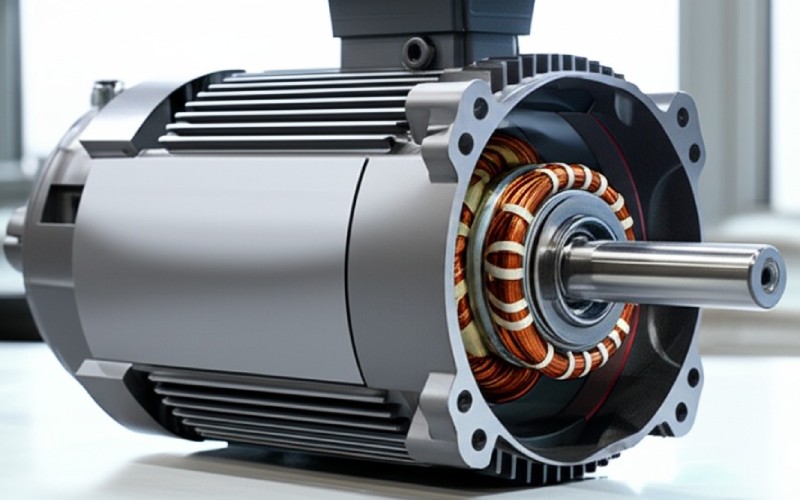
Now, let’s talk about the radial flux motor. This kind is what most of us know. It has been the standard for decades. Think of a can shape. That is often what a radial flux motor looks like. This radial flux design is common. It also has a stator and a rotor. But in this machine, the magnetic flux moves out from the center. It moves like spokes on a wheel, going radially. This radial flux is different from the axial flux way.
This traditional radial flux motor is very common. You find this motor in many things. The stator in a radial flux motor is often a cylindrical shape. Its radial flux path is key. It has slots for copper windings. The rotor spins inside this stator. The magnetic forces push and pull to make it work. It’s good, but it can be long. Sometimes we need a shorter motor. Radial flux machines are very common.
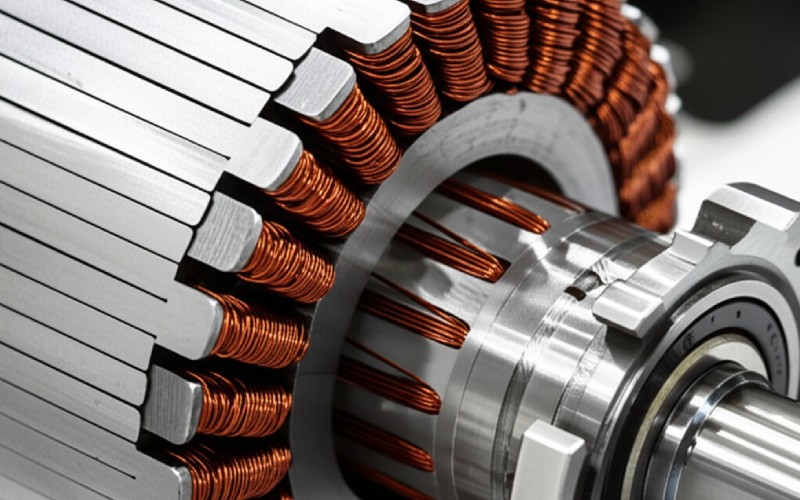

Let’s look at how the magnetic power moves. This is the magnetic flux path. In an axial flux motor, the magnetic flux flows axially through the stator. This means it goes along the length of the motor’s axle. Imagine it going from one flat plate to another. This path is short and direct. This can make it very strong for its size. The magnetic field is key here for this axial flux motor.
Now, think about the radial flux motor. Here, the magnetic flux flows radially. It goes from the inside to the outside, or outside to inside, across the air gap between the stator and rotor. This magnetic flux path is different for the radial flux motor. It travels around the motor, circumferentially in a way, through the stator core and yoke. This is how most electric motors we see every day work. These flux machines work well. This shows the clear axial vs radial flux difference.
Let’s peek inside these motors. The stator is a very important part. In an axial flux motor, the stator is often a disc. It holds the wires. These wires can be copper windings including hairpin windings. The magnet parts, often permanent magnet pieces, are on the rotor discs. These rotors and stators face each other. The electromagnetic force is very strong between them. It can have one stator and two rotors, or two stators and one rotor. This topology can change for an axial flux motor.
In a radial flux motor, the stator is usually a ring. This radial flux construction is typical. It has slots, or stator tooth shapes, cut into it. The copper wires go into these slots. The rotor, with its magnet or its own coils, spins inside this stator ring. The magnet on the rotor has north and south poles. The magnetic pull happens across the small gap. The way the magnet is placed on the rotor is key for this device. This is a common machine.
Yes, the axial flux motor design is quite special. Its flat shape makes the motor design different. Because the magnetic power goes along the axle in an axial flux motor, the parts can be made flat. This means it can have a short axial length. This is good for making a compact motor. The design needs careful thought about the forces from the strong magnet. These forces want to pull the flat parts of the axial flux motor together.
This motor design also means we can use less material sometimes. For the stator structure, we might not need as much heavy iron. Some axial flux motor designs use powder metal. The features and performance depend a lot on this specific motor design. It’s a key part of electrical engineering to get this right. The goal is a high-performance motor. The axial flux itself defines much of the motor.
You might hear about something called SMC. SMC stands for soft magnetic composite. This material is made from ferromagnetic iron powder particles. Each tiny piece of iron has a coat on it to insulate it. This is useful for making parts of a motor, like the stator. Using SMC allows us to make complex shapes, not just simple 2-dimensional forms. This is harder with traditional laminated electrical steel.
Why use soft magnetic composite in an axial flux motor? Well, SMC can help guide the magnetic power very well. It can make the motor lighter. It can also help reduce some energy losses in the motor. For an axial flux motor, where the magnetic path can be tricky, SMC is a good choice. This material helps build a better axial flux machine. The use of SMC is one of the advantages of axial flux types. The stator benefits from this magnetic material.
So, what are the big wins for an axial flux motor? One big thing is its shape. It is flat and wide, not long and thin. The outer diameter can be large. This means a shorter axial length. This compact structure is great when space is tight. Think about putting a motor in a wheel. An axial flux type can fit well. It often has high torque. High torque means strong twisting power from the magnet and stator setup. This axial flux type often has that.
Another plus for axial flux motors is power density. This high power density means you get a lot of power for its size and weight. They can also have higher efficiency. This means less wasted energy. The magnetic path is short, which helps. This can reduce end effects and save winding copper. For some EV applications, these motors offer good potential. The potential of axial flux motors is very exciting for new types of machines, even a generator. This axial flux technology is growing.
Yes, a radial flux motor can still be a great choice. These machines have been around for a long, long time. We know how to make them well. They are often cheaper to make. For many jobs, a radial flux motor works just fine. The radial flux principle is sound. This type is the standard for decades for good reasons. It is a strong and trusty machine.
The radial flux motor design is well understood. This radial flux approach is reliable. Making the stator with lamination is a common way. This design handles heat, the thermal part, pretty well too. If you don’t need a super flat motor, or the very highest twisting power for its size, then radial motors can be perfect. They are used in so many things, from fans to big machines. These electric motors are workhorses. The radial flux design is proven.
When we talk about power, we often mean how much work a machine can do. An axial flux type can give very high torque. This is strong turning force. Because they can be wide, they can have a large area for the magnet parts to work. This axial flux approach is strong. This helps make more torque. The magnetic field in these motors is strong. This type is often a permanent magnet design. Each magnet helps, and sometimes these use rare earth materials for more power.
A radial flux permanent magnet motor is also strong. Many high-power electric cars use this kind of machine. It can be built to give lots of power and good speed. Comparing them, an axial flux type often has better torque density. This high density of torque is a benefit, especially compared to radial flux motors of similar output. This is a big reason for the interest in axial flux machines and their specific axial flux path. The specific electric motor design matters a lot too. The radial flux path in a radial flux permanent magnet motor is also efficient.
This is the big question: axial flux vs radial flux, which machine to pick? It depends on what you need your motor to do. Do you need a very flat motor? Is light weight very important? Is high torque a must? If yes, an axial flux motor might be your winner. The axial flux path in an axial flux motor is key. This axial flux type works well for electrification in new areas. Many are looking at this axial flux motor type for things like drones or even wind turbines as a generator. The axial flux design is good here.
But, if cost is a big worry, or if you need a machine that is easy to make in large numbers, the traditional radial flux motor is often a safe bet. These radial flux types of motors are well known. The choice of motor also depends on other things. Think about how it will be cooled (thermal management). Think about the speeds it needs to run at. Many are a type of BLDC motor. There are many synchronous motor options. The radial flux way is tested.
For your specific electric motor design, list what is most important. Is it compact size? Is it energy efficiency? Is it the total KW of power? Both axial flux and radial flux motors have their place. The best machine is the one that fits your needs. Maybe it’s an axial flux type. Or maybe a radial flux type. Some new designs even try to mix ideas from both types of motors. For example, some axial motors use various types of copper. There are many types of copper windings including hairpin windings, which help boost performance. These various types of copper windings are chosen carefully. Understanding the differences in features and performance for each motor topology is key. You might even find a patent for a new motor idea! The axial flux motor continues to evolve.