Let Sino's Lamination Stacks Empower Your Project!
To speed up your project, you can label Lamination Stacks with details such as tolerance, material, surface finish, whether or not oxidized insulation is required, quantity, and more.

Have you ever questioned what makes an electric motor spin? A huge part of several common electric motors is something called a squirrel cage rotor. It seems funny, right? But it’s a very crucial item. In this short article, I’m mosting likely to tell you all about the building and construction of the squirrel cage rotor . We’ll take a look at what it’s made of and exactly how it’s put together. Understanding this aids us to recognize how effective induction motor jobs are. Believe me, it’s easier than you think, and it’s why these motors are almost everywhere! This short article is worth reading due to the fact that you’ll find out the secrets behind a tool that powers so much of our world.
Put simply, the rotor is the revolving component of an induction motor . Think about a rotating top; the rotor resembles that, yet it’s inside the motor . The rotor is a key piece that helps transform electric power into mechanical energy. This movement can after that do work, like turn a follower or run an equipment. The induction motor needs this spinning rotor to do its job. The rotor rests inside the stator . The stator is the stationary part of the induction motor . The rotor is generally a cylindrical form. It’s mounted on the motor shaft . When the rotor rotates, the shaft rotates as well. This shaft after that attaches to whatever the motor is meant to relocate. So, the rotor is really the heart of the action in an induction motor . Recognizing the rotor is the first step to understanding the whole induction motor . Several induction motor kinds make use of a specific kind of rotor .
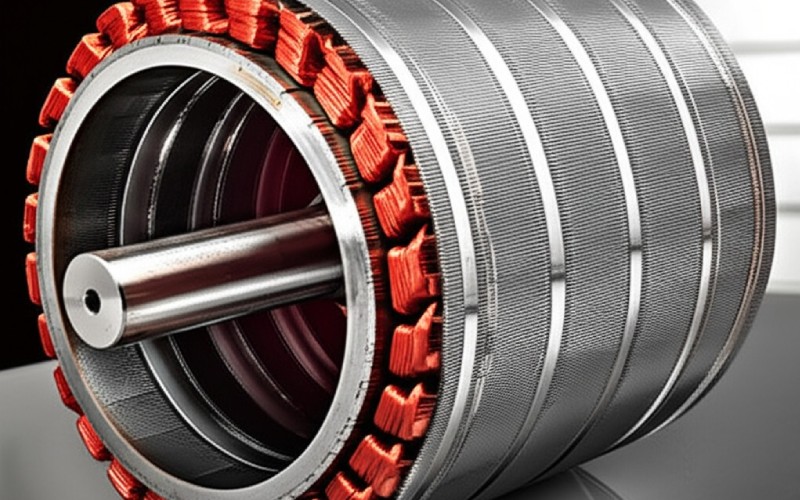
Why the name ” squirrel cage rotor “? Well, if you could take the core component of the rotor out and check out its electrically conducting components alone, it would certainly look a bit like a cage. You understand, the sort of cage a family pet squirrel or hamster could run in. This “cage” is constructed from conductive bars that run the length of the rotor. These bars are after that connected at both ends by a ring , called an end ring . So, you have these identical bars and 2 rings holding them together. This structure is what provides the squirrel cage rotor its name. It’s a basic but extremely brilliant design. This cage rotor design is really typical in a squirrel cage induction motor . It’s a rugged design, which implies it’s strong and lasts a long period of time. The basic name truly helps people picture what this component of the induction motor resembles. The rotor spins, and this cage framework is essential to just how it works with the stator’s magnetic field.
The core of a squirrel cage induction motor rotor is not just a solid item of metal. These slices are called laminations . Think about a deck of cards; the rotor core is like that, yet with steel lamination sheets. These steel laminations are stacked together to form the cylindrical shape of the rotor core. There’s a great reason for this lamination style. Making use of laminations helps to reduce energy losses in the induction motor . These losses are typically as a result of something called eddy currents. An eddy current is an unwanted current that can flow in the metal. By using thin, insulated laminations , these eddy currents are maintained little. This makes the squirrel cage motor more efficient. The rotor core also has ports cut into it. These slots in the rotor are where the rotor bars will go. The whole rotor building is thoroughly intended.
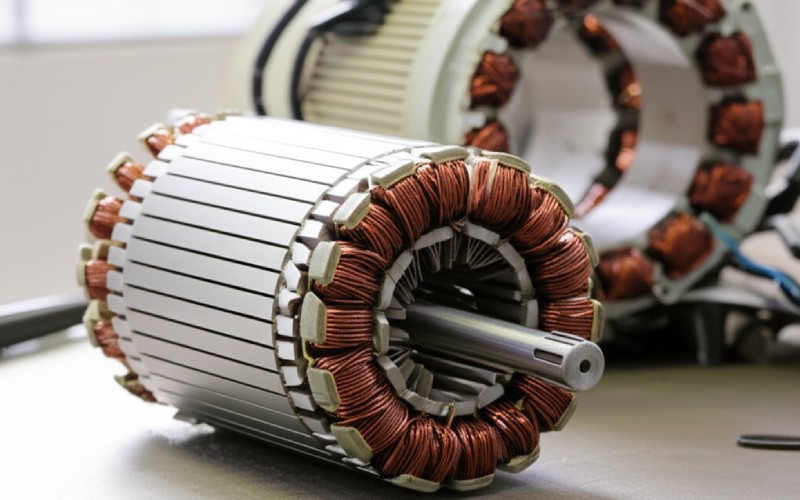
Currently, let’s discuss the “cage” component of the squirrel cage rotor . The rotor bars are very important conductive bars . They are placed into the slots on the rotor core we simply spoke about. These rotor bars are often made of aluminium or sometimes copper . Aluminium is common because it’s light and performs electrical energy well. For larger motors , copper bars may be used because copper is an even far better conductor. At each end of the rotor core, these rotor bars are all attached together. They are connected by what we call end rings or shorting rings . Picture the bars as the straight components of the cage and the end rings as the circular items that hold them entirely. These end rings create a closed electrical path for the current to stream through the rotor bars . This finishes the “cage” framework. The rotor bars and end rings together create the rotor winding , despite the fact that it looks very different from the coiled winding you see in a stator . This is a key component of exactly how the squirrel cage induction motor works.
This is where the “induction” part of an induction motor comes in. The rotor bars in a squirrel cage rotor are not directly attached to any kind of outdoors source of power with wires, like the stator winding is. Instead, the current in the rotor is “generated.” This means it’s produced by an altering magnetic field. The stator of the induction motor has its own winding . When AC power is supplied to the stator winding , it develops a rotating magnetic field . This rotating magnetic field from the stator sweeps past the rotor bars . Due to the fact that the rotor bars are conductors, this changing area causes a voltage to be generated in them. Given that the rotor bars are short-circuited by the end rings , this voltage makes a current flow via the bars and rings . This current induced in the rotor bars then creates its own magnetic field. The two electromagnetic fields (from the stator and the rotor ) interact, and this makes the rotor rotate! The rotor circuit is completed by the end rings . The speed of the rotor will constantly be a little much less than the speed of the rotating magnetic field; this distinction is called slip . This slip is needed to induce the current.
But there are various types. One of the most usual is the solitary cage rotor we have actually been talking about. Nevertheless, for some special jobs, engineers created something called a double squirrel cage rotor . This type of rotor has 2 sets of “cages” or rotor windings on the same rotor core. Why two cages? Well, a double squirrel cage rotor can give the induction motor better starting torque. Starting torque is the twisting pressure the motor has when it first launches. One cage, usually the external one, is made with higher resistance material. This aids with good starting torque and limits starting current. The inner cage has lower resistance, which benefits running efficiently at regular speed with low slip . So, a double squirrel cage style attempts to get the most effective of both globes. This is a clever method to transform exactly how a squirrel cage motor behaves for different jobs. This classification of rotor allows for even more specific induction motor designs.
Often, when you take a look at a squirrel cage rotor , you could observe that the rotor bars (and the rotor slots they are in) are not flawlessly parallel to the motor shaft . Instead, they are slightly slanted, or “skewed.” There are a couple of excellent factors for doing this. One main factor for the skew is to make the induction motor run even more smoothly and silently. If the rotor bars were straight, they can associate the stator teeth simultaneously as the rotor spins. This can cause jerky motion and even more noise. Skewing the rotor bars implies they get in the electromagnetic field from the stator more gradually. This helps in reducing sound and vibration. Another benefit of a skew is that it can stop the motor from obtaining “stuck” at certain rates (a phenomenon often called cogging), specifically throughout motor starting . It also assists to offer a much more uniform torque . So, that mild skew in the rotor construction makes a big distinction in the induction motor’s performance.
The squirrel cage rotor is super usual, but it’s not the only type of rotor out there for an induction motor . There’s additionally something called a “wound rotor.” A wound rotor is different due to the fact that, instead of solid rotor bars , it has actual coiled windings, just like the stator winding . These windings are after that connected to slip rings on the shaft . Brushes ride on these slip rings , permitting exterior resistors to be linked to the rotor circuit . This gives even more control over the motor’s speed and starting torque . So, a wound rotor induction motor provides more speed control yet is much more complex and expensive than a squirrel cage induction motor . After that there’s the synchronous motor. A synchronous motor rotor is also very different. It usually has defined magnetic poles, either made by permanent magnets or by providing DC existing to a rotor winding (once again, commonly with slip rings ). The key aspect of a synchronous motor is that its rotor rotates at the exact same speed as the rotating electromagnetic field from the stator — it performs at a continuous rate with absolutely no slip under typical load. A squirrel cage induction motor rotor always has some slip . Also a generator can utilize designs similar to motor rotors, however its function is to create electric power. A squirrel cage rotor is simpler and more rugged than these other rotor types.

While we have actually focused a great deal on the fantastic squirrel cage rotor , it is necessary to keep in mind that an induction motor has one more very integral part: the stator . The rotor is the spinning part, yes, but the stator is the stationary part that surrounds the rotor . The rotor rests inside the stator . The stator is likewise made from laminations to lower eddy current loss. It has its own collection of windings made from insulated cable, normally copper . When you connect a three-phase (or solitary stage for smaller motors) AC supply to the stator winding , it produces the turning electromagnetic field . This field is what “generates” the existing in the squirrel cage rotor and makes it transform. So, the stator and rotor collaborate like a team. The stator produces the magic area, and the rotor responds to it. Both are necessary for the induction motor to operate. The motor framework holds both the stator and the rotor assembly (which includes the shaft ). The interaction between the stator’s magnetic field and the current caused in the rotor conductors is the heart of exactly how an induction motor jobs.
The main thing is their straightforward and rugged rotor construction. The squirrel cage rotor has no brushes (unlike some DC electric motors or wound rotor motors), no slip rings (unless it’s a specialized wound rotor that sometimes obtains contrasted, but real squirrel cage induction motor does not have them), and no moving electrical contacts on the rotor itself. This makes it really reliable and implies it needs extremely little maintenance. Since the rotor construction is easy, making use of aluminium or robust copper bars and end rings, it’s also cheaper to make. These phase squirrel cage induction motors (specifically 3 phase squirrel cage induction types) are efficient, can perform at a nearly continuous speed under differing loads (though there’s always some slip ), and have good starting torque for numerous jobs, especially if they use designs like the double squirrel cage . They can be made in a substantial series of sizes, from tiny ones to large ones. This mix of affordable, high dependability, and good efficiency is why the squirrel cage motor is a workhorse in industries all over the globe. The rotor style is a big part of that success. You can install this type of induction motor in many ways. The absence of insulation concerns for the rotor winding (as it’s just bars) also simplifies things. Many electric motors can also be developed for reduced-voltage starting.